What if you could combine the digital and physical worlds into a single experience that could flow as one? This is what spatial computing allows us to do. This newborn technology will alter the way humans interact with computers, enabling uniquely intelligent, immersive, and feel-like-our-natural-environment experiences.
So, what is spatial computing? It’s more than a buzzword; this is the linking of real-world space to being imbued with digital intelligence through technologies including AR and VR app development, AI development services, and enhanced sensing capabilities. By understanding gesture, movement, and context, this computing replaces screens with interactions that can be felt, given the right conditions.
Spatial tech and its interactions are being witnessed by businesses, developers, and consumers across multiple industries: healthcare, education, retail, and entertainment. As the trend makes its way, it is also redefining the art of communication, learning, and creativity.
Whether you are just curious about how it works, what it can do, or what platforms are available, this guide is meant to illustrate that computing may be as intelligent as a leap forward in technology.
Market Size and Future Projections for Spatial Computing
According to Grand View Research, the global spatial computing market is expected to reach $469.8 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of about 20.4% from 2023 to 2030. The primary drivers of growth include increased demand for immersive experiences, along with innovative growth across other industries.
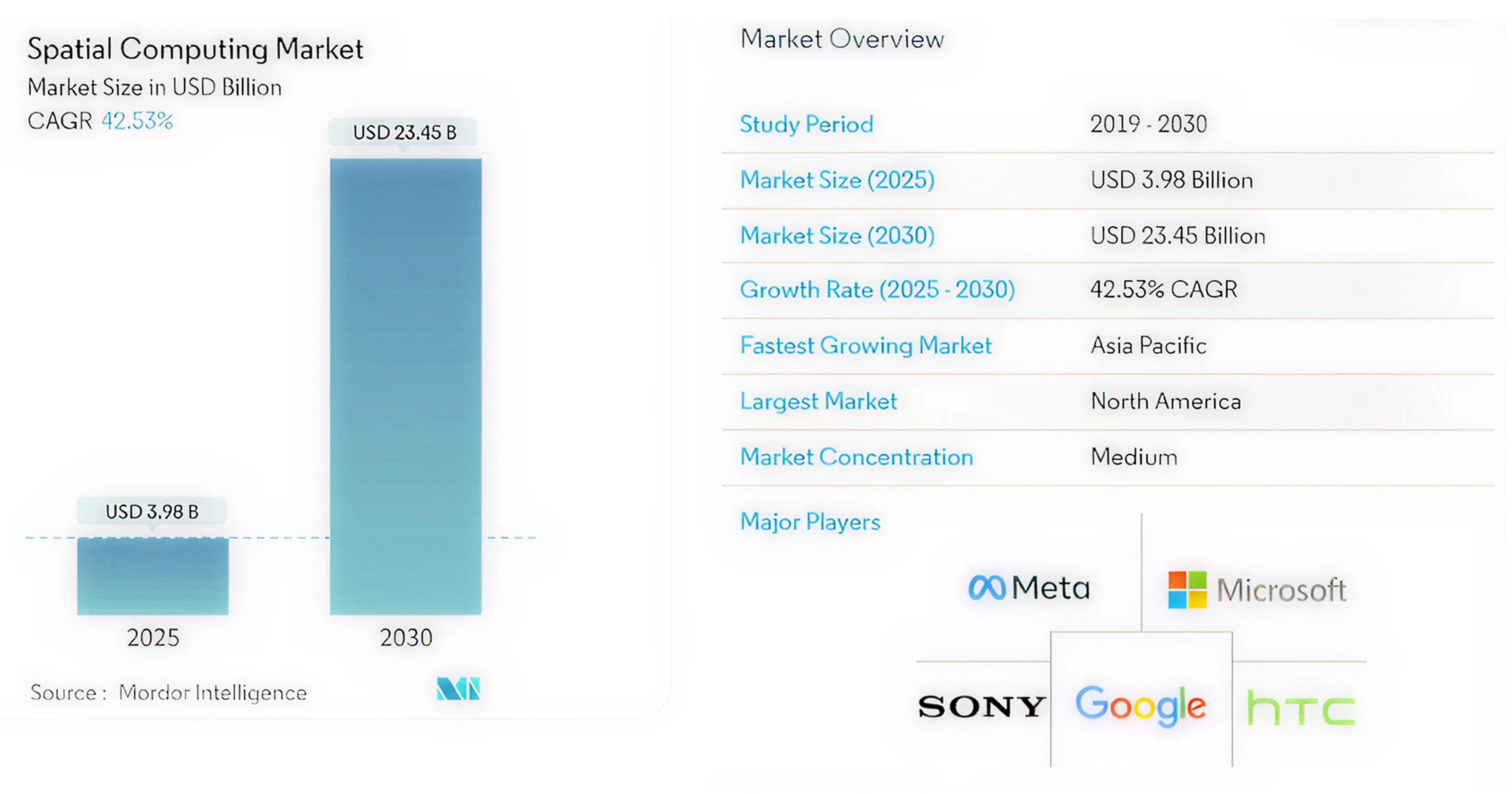
Some additional industry outlooks project that the global market will grow from $3.98 billion in 2025 to $23.45 billion by 2030, indicating a strong CAGR of 42.53%, as Asia-Pacific leads that effort through the adoption of 5G tech and region-led investment. (Source – Mordor Intelligence).
By 2025, the US computing market is expected to be valued at $226.6 B, driven by investment from leading technology companies and the use of public-private partnerships in developing AR, VR, and artificial intelligence.
The spatial computing segment that relates to AR, VR, and directly associated markets is expected to grow indirectly to an even larger reach of $85.56 by 2030 and a CAGR of 33.16%. This may come especially from applications in the enterprise, education, and healthcare sectors.
What is Spatial Computing?

Spatial computing refers to a technology that fuses the physical and digital worlds of the space around us and creates interactive experiences. In this case, the question of what is spatial computing? These are systems that understand space and allow digital objects to interact with the real world. This idea is the concept of how we view interaction between humans and machines, and how our connection with the environment around us will change over time.
In the 3D interaction definition, it is about the ability of computers to process, interpret, and respond to data from real 3D spaces. Think about it: using gestures to control digital content, voice commands, or even using your eyes to look at what you want to engage with, this is part of the concept of this computing meaning the thinking and direction of technology is more human-centered and human-like in thinking.
In terms of “how does spatial computing work”, it consists of advanced tools such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing that make all of this happen. When you have all of this technology together, the device senses depth, maps a space, and allows you to overlay digital content to the real world, removing barriers that have stifled potential interactions in ways of thinking.
How Did Spatial Computing Start and Where Is It Headed?
The journey has been around for many years now, and it has developed into a powerful factor that is significantly changing the way humans interact with technology. The overall history of spatial computing actually started with simple 3D graphics and ended up with very engrossing AR and VR experiences. To date, the spatial computing technology landscape that is currently at the forefront of the industry is already combining hardware, AI, and cloud innovations.
1. Early Foundations
The idea started with 3D modeling and simulation tools that opened the door for digital interaction with the real world.
2. AR and VR Integration
AR and VR were the main driving forces behind the popularity of immersive computing, which, at the same time, made it possible for people to live in a more connected, albeit virtual, environment.
3. Industry Milestones
The combined power of hardware and spatial software in the hands of companies like Apple, Nvidia, and Google led to faster innovations.
4. Metaverse Expansion
The adoption of spatial computing in metaverse was one of the things that transformed collaboration and the whole concept of virtual socializing.
5. Looking Ahead
The future of spatial computing will be one of more intelligent and communication-friendly experiences that will be driven by AI and the latest devices in the market.
Core Technologies Behind Spatial Computing
Spatial computing is an integration of multiple innovations, thus making the digital content embedded in the real world seamless. The whole process is going to be based on advanced systems, which will change the way humans interact and will also make the interactions between humans and machines more like human ones. Enabled by AR, VR, AI, and the cloud, which together provide the power of computing with full immersion.
1. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
By augmenting the real-world environment with digital inputs, AR provides a mixed-reality experience, and VR offers an entirely virtual one. These two systems are at the core of spatial computing and let the user interact and feel the 3D world through visuals, touch, and communication simultaneously.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI never sleeps and keeps on learning, so it processes more and more input and gets clearer and clearer with time. AI assists the spatial domain management by making it real-time and thereby achieving the highest level of accuracy and responsiveness that is possible with the technology in question.
3. Spatial Cloud Computing
The cloud will provide infrastructure that allows the 3D spatial data to be stored and managed in huge amounts, besides allowing very large and very smooth experiences for the interconnected machines and platforms.
4. Computational Power and Hardware
The high-end gadgets of the day, like 3D interaction glasses and headsets, support the transformation of visual experience. On one hand, Apple spatial computing and Nvidia spatial computing technology are venturing into the new world of immersive computing and will not only bring high-performance devices but also immersive interaction, driving innovation along with 3D interaction technology.
How Immersive Computing Works?
Immersive computing is a technology that connects the digital and physical worlds by making real-time interactions that are natural and human-focused. To comprehend how does spatial computing work, it is necessary to know how the different elements, like sensors, AI, and real-world data, work together to change perception and engagement in different places.
1. Real-time Data Collection and Processing
The system that utilizes motion detectors, cameras, and spatial computing AI is permanently monitoring users’ movements, gestures, and spatial coordinates. The unchanged data flow helps the device to know the depth, movement, and location of the object, hence making the experience responsive and lifelike.
2. Immersive Interactions
By means of immersive computing, the user has the opportunity to control more than just the screen. The whole process from voice commands to touch to hand gestures makes it possible for the individual to interact with 3D digital objects, which are projected as the real world around them. This results in not only a more natural and engaging way to work and communicate but also a richer one.
3. Applications in the Metaverse and Beyond
The merger of spatial computing and metaverse brings users together in a virtual world where they can chat, work together, and be creative at the same time. Apart from entertainment, the application of spatial computing in healthcare industry improves the quality of visualization and the precision of the physical world, which benefits surgeons, medical students, and therapists.
Real-World Applications of Spatial Computing
The expansion of 3D interaction applications is changing the way people work, learn, and engage across sectors. By situating digital intelligence in physical spaces, spatial computing is enabling organizations and individuals to engage at a new level of immersion and productivity. These spatial computing use cases exemplify its effects in healthcare, education, and enterprise.
1. Spatial Computing in Healthcare
Spatial computing in healthcare powered by AI in healthcare, is used to support doctors via 3D medical imaging, guided surgery simulations, and virtual health consultations. Using spatial tech, doctors can visualize complicated anatomy to perform correct and safer procedures.
2. Spatial Tech in Education
Students and educators now have the ability to utilize virtual classrooms or 3D lessons that help to make the learning experience come alive. Interactive study tools that are developed with a spatial computing application are helpful in bridging the learning opportunities available to students, whether they are learning remotely or in person.
3. Immersive Computing in Enterprise
Businesses are now integrating enterprise AR tools integration with spatial computing platforms that enhance conceptual learning in collaboration, training, and maintenance. In doing so, collaborative tools like AR create a shared digital workspace, which allows teams to make quicker, data-driven decisions via spatial collaboration in real-time.
Future of Spatial Computing
The spatial computing future will not only alter the way humans communicate with the help of technology but also provide a gradual and natural transition between the physical and the digital.
Technologies like AI, increased connectivity, and better hardware are the main players in providing the world with rich immersion and powerful and new possibilities for both businesses and consumers.
Spatial computing 2025 will, to a great extent, contribute to the global distribution of activities through the establishment of new channels of communication, modernized ways of learning, and transformed work environments.
1. Next-gen Technologies
The deployment of 5G networks, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), and the introduction of 3D interaction headsets will together result in the increase of computing power, the reduction of delay, and the provision of richer interactive content. So the technologies will make the spatial experiences more natural and easier to handle.
2. Metaverse and Spatial Computing
Spatial computing and metaverse keep on changing; moreover, their interaction leads us to imagine a future where digital worlds that are persistent and shared will be an indispensable part of life.
The people will participate in the creation of networks and collaboration in various, rich in details, and even more, physical-like places which are quite distinct from one another, and these places will coexist with the real and virtual ones, thus changing the nature of social and business interactions.
3. Scalable Platforms
The rise of scalable spatial computing platforms will facilitate developers and enterprises in realizing the eco-friendliness of immersive solutions across gadgets, tech, and environments.
By the year 2025, these digital platforms will not only be hubs of innovation but also empower and expand the capabilities of the enterprises that rely on spatial awareness and real-time intelligence.
Ethics and Social Implications
As 3D interaction becomes part of everyday life, discussions around responsibility and fairness have grown stronger. The very basis of the ethics of spatial computing lies in the area of personal data, which this technology collects, interprets, and uses. The dominance of this technology is accompanied by the very fundamentals of transparency, protection, and inclusivity.
1. Privacy and Data Security
The greatest concern is the spatial computing privacy issues around the fact that the devices, through Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality, collect location, movement, and behavioral data. Not having very strict regulations in place, the information is prone to misuse and abuse, which would result in security risks and identity concerns.
2. Digital Divide
The digital divide in immersive computing is a reflection of the difference between the developed regions that can afford the latest technology and the underdeveloped ones that cannot. The unequal distribution of access to spatial technology may eventually lead to an increase in global economic and educational inequalities.
3. Ethical Concerns
The social impact of spatial computing has spread to such issues as AI model biases, a stronger reliance on virtual environments, and a lesser degree of direct communication among people. To promote a society where everyone has access to spatial technologies, it is the companies’ and governments’ responsibility to guarantee a balanced and fair development of the technology.
Environmental Impact of Spatial Computing
The environmental impact of spatial computing is a mix of its challenges and its potential for good. Once the technology reaches its peak, the world will be left with no option but to prioritize the coexistence of innovation and an environmentally friendly approach. The path to the sustainability of immersive computing has become relevant more than ever, ranging from energy-heavy data systems to the use of green digital solutions.
1. Sustainability Challenges
It is the large-scale use of spatial computing sustainability with the operation of a VR headset and a data center that together use large amounts of electricity, thus increasing carbon emissions. Building greener infrastructures and energy-efficient gadgets will be the main aspect of cutting down the overall environmental footprint of these technologies.
2. Green Tech Applications
Among the wonders of 3D interaction, one of its facets is to help achieve spatial computing green tech that shares its blessings with a few environmental sectors, like smart city planning, waste management, and the building of sustainable structures. In this context, digital twins and immersive simulations are helping cities do so by optimizing their energy use and minimizing resource wastage.
3. Recycling and Hardware Waste
The fast production of headsets and sensors may lead to the emergence of electronic waste. In this regard, companies are now looking into reusable materials and modular hardware as a strategy for promoting the circular economy in spatial computing devices.
4. Energy-Efficient Innovations
The introduction of AI-driven optimization technologies and the setting up of data centers powered by renewable energy are evidence that immersive computing can be developed in a socially conscious way if clean energy sources are adopted. Efficient processing and distributed computing are two techniques through which the reduction of long-term energy reliance is made possible.
DIY Spatial Computing: How You Can Get Started
Exploring spatial computing doesn’t require high-end labs or advanced systems anymore. The tech crowd can now come up with DIY immersive computing projects with the help of commercial-grade online communities and basic coding skills. The ever-increasing ecosystem of development kits, resources, and spatial computing courses, to name a few, has made it very easy for beginners to find their way into this field of technology.
1. Accessible Tools
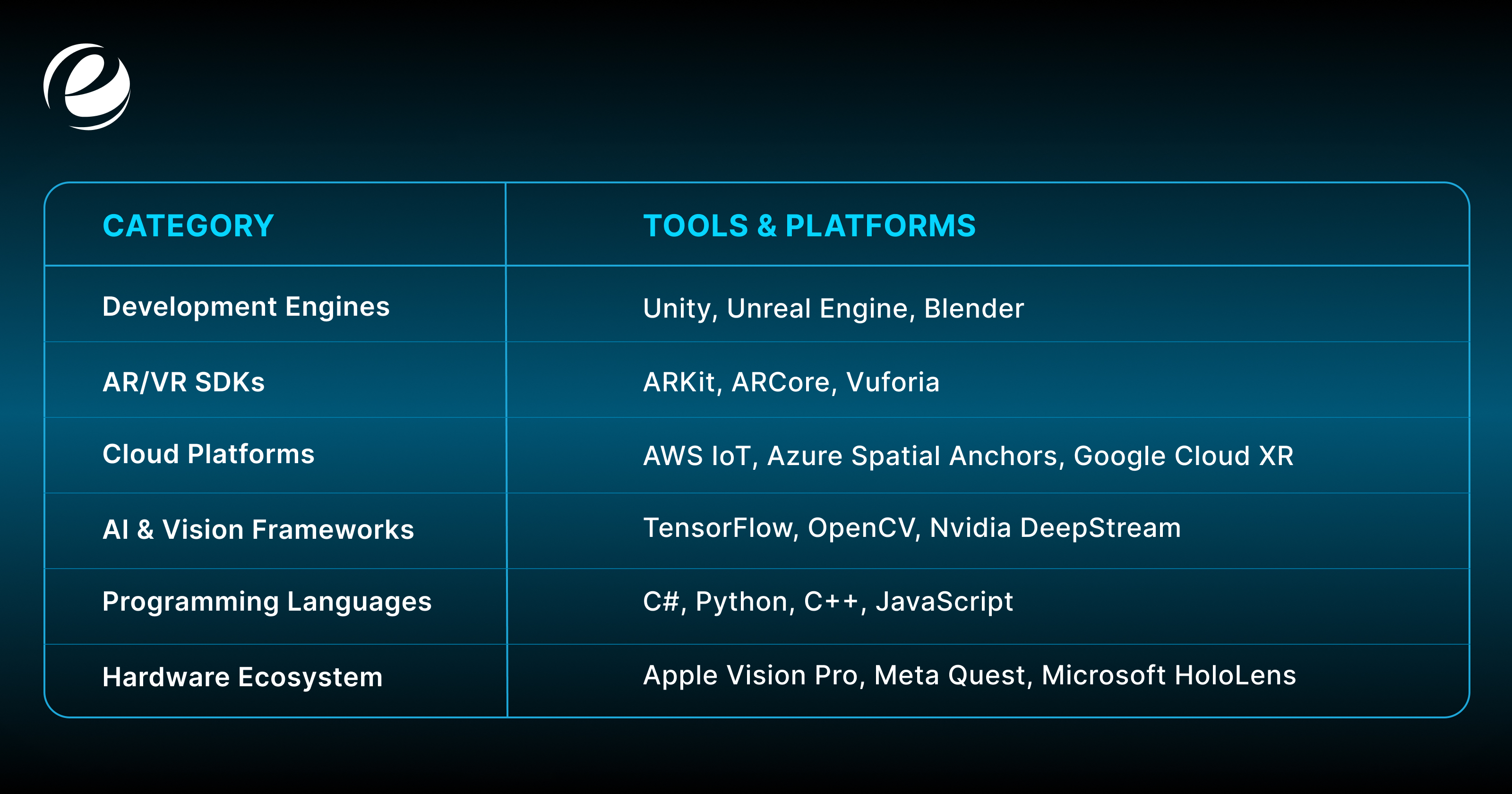
Applications such as Unity and ARKit are not only for professionals but also for beginners who want to learn how to start with AR and VR gradually. They offer different types of easy-to-use tools, such as visual editors, already-made assets, and tutorials that will help you deal with the complicated functions of the 3D interaction area.
2. Building Simple AR/VR Experiences
Beginners could start by creating 3D models that respond to touch, employing motion tracking, and running their applications on either mobile or headset devices. The trial-and-error learning process gives one a strong hold on more advanced projects.
3. Learning Pathways
A number of spatial computing courses and online boot camps are providing training in basic AR/VR development, 3D modeling, and AI integration. These resources facilitate real-world applications at the same pace as the learners.
4. Experimentation and Community
Collaborating with others in spaces like developer forums and open-source projects will enable the learners to share their thoughts, and hence, they will grow faster in the spatial computing community. Experimentation is the main source of creativity and also the most practical means of understanding.
Hidden Costs of Spatial Computing
While spatial computing holds the potential for innovation and convenience, it also raises challenges that are often unacknowledged. Hidden costs of immersive computing originate not only from the hardware and software of systems, but also from the financial, psychological, and social costs of human life. Being aware of these factors will help us all achieve equilibrium between advancement, speed, and responsibility.
1. Financial Investment
There is significant financial investment related to the development and operation of spatial computing systems, including: infrastructure, hardware (and peripheral devices), and software applications. There are considerable costs associated with adopting 3D interaction for small businesses, including the cost of cutting-edge headsets, sensors, and development tools.
2. Psychological Effects
Long-term use of immersive environments may cause fatigue, a decrease in real-world interactions, and contribute to other mental health-related issues. Recognizing the potential spatial tech psychological impact serves as a valuable reminder for moderation and digital well-being.
3. Social and Economic Disruptions
Although more economic opportunity exists as a result of 3D interaction, it can also contribute to economic displacement. Emerging job categories in AR/VR may create economic impact of spatial computing, but increasing automation and immersive tools can replace traditional jobs and stabilize the workforce globally.
4. Energy and Maintenance Costs
Data-compatible systems consume a great deal of energy, forcing systems to be continuously and/or regularly updated, bringing complexity and cost to operations and the ecosystem.
5. Ethical Responsibility
Organizations in the spatial computing domain share an ethical responsibility to balance responsibility and digital friendliness, privacy, inclusivity, fairness, and all of the negative factors connected to immersive computing so that they don’t deepen social inequities.
Leading Companies in Spatial Computing
The worldwide ecosystem of spatial tech companies is getting bigger and bigger at a fast pace, with the involvement of both the big tech companies and the new spatial computing startups changing the way people will communicate with the digital world.
The major players in the industry are taking the next step in the realm of immersive technology by way of their new devices and the use of cloud technology in the form of artificial intelligence.
1. Apple Vision Pro and Beyond
With the announcement of Apple Vision Pro, Apple spatial computing has solidified its position as the main player in Apple’s immersive computing. Merging AR with top-notch sensors gives out mixed reality visuals that unite the physical with the virtual worlds.
Likewise, Meta isn’t far behind and sets the pace in VR collaboration through various means, while Nvidia spatial computing concentrates on equipping 3D interaction with powerful GPUs along with AI-assisted rendering, thus allowing the creation of real-time 3D environments.
2. Startups and Innovation
More and more new ventures are coming up in the spatial tech area using this technique, such as AI training and Zoom collaboration. Their flexibility gives rise to faster trials and creative problem-solving.
3. Partnerships and Ecosystems
The collaboration of hardware manufacturers, cloud service providers, and software developers has led to the creation of strong networks that support the building of spatial computing solutions that are scalable for industries such as healthcare, education, and entertainment.
4. R&D and Global Expansion
Constant research and cross-industry investment are the main factors behind the global adoption of spatial computing, thus making the technology accessible to the latter’s clients and consumers all over the world.
Why Partner With Us?
At Emizen Tech, we combine inventiveness, know-how, and hard work to make businesses more competitive in the digital universe. The solutions that our team creates are high-tech and easy to use, and they are in good harmony with your objectives while providing results that can be quantified.
Whether we are developing software that can grow with the demand, mobile applications that are very interactive, or bringing in the latest technologies like spatial computing, we make your dream come true through both accurate and creative means.
Our approach is that through partnership, we can attain success. Partnering with EmizenTech affords you the benefit of a team comprising highly skilled developers, designers, and strategists who are in close proximity to you throughout. Our method guarantees flawless execution and adds value over the long run from the very early phase of planning and design through to deployment and ongoing support.
Our persistent endeavor for premium quality, breakthrough, and client contentment is globally recognized as a reliable tech partner for companies. By partnering with EmizenTech, you are not just making a technological investment, but you are also getting a team that comprehends your business, thus enabling it to grow faster, smarter, and stronger.
Why Spatial Computing is the Future of Technology?
The spatial computing future is a significant pivot in mankind’s technological interaction. It is a circle that encloses the digital and the physical, thus making possible the cross-industry communication, teaching, and productivity even in such varied sectors as health, schooling, and entertainment, not to mention the enterprise. The spatial computing revolution is bringing about a new generation of environments, smarter and more interconnected, that are changing the daily routine of people into a reality that is immersive and data-based.
To comprehend the importance of immersive computing is a must for individuals and organizations eager to remain up-to-date in the digital transformation era. Its usage is one of the reasons that progress is being made in the areas of innovation, creativity, and collaboration globally.
The right moment for the exploration and experimentation of spatial computing technologies has finally come. Keep yourself updated, accept the changes, and route your sector’s progress via this revolutionary technology that is going to shape our digital future.
FAQs
What is the role of AI in spatial computing?
AI is the leading technology that permits machines to understand the real world and respond to it. The interaction of spatial computing and AI mainly consists of data analysis, object recognition, and prediction, which eventually result in the provision of smart and engaging digital experiences to the users.
How does immersive computing work in healthcare?
Doctors are more accurate in their surgical ways, patients can be attended to telephonically from farther places, and trainers of medical students can provide the latter with 3D visualizations and AR simulations thanks to 3D interaction.
What are the best spatial tech headsets?
The list of the best spatial computing headsets includes Apple Vision Pro, Meta Quest 3, and Microsoft HoloLens 2. All the listed devices are capable of delivering lifelike images, precise tracking, and advanced interaction tools to the users.
What are the main benefits of spatial computing?
Immersive computing facilitates and enriches learning, communication, and productivity by bringing in the aspect of interactivity and efficiency in tasks through the integration of physical spaces with digital content, thereby having a significant impact on them.
Is spatial computing expensive to adopt?
The costs vary depending on the hardware and software required to support the processes. Advanced systems may still come at a premium, but the new tools and platforms are designed more affordably, hence becoming available not only to professionals but also to students.




